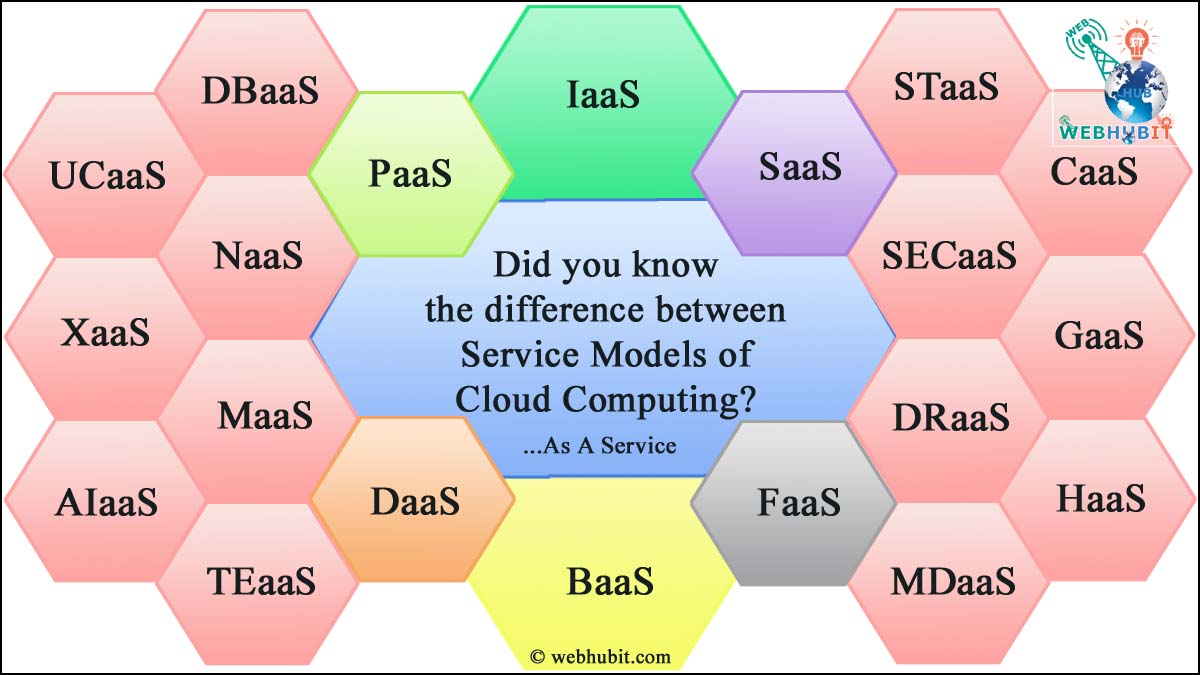
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, various service models have emerged to cater to diverse business needs and requirements. From infrastructure to software and security, the cloud offers a plethora of services that can transform the way organizations operate. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of different cloud service models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), Desktop as a Service (DaaS), Function as a Service (FaaS), Backend as a Service (BaaS), Database as a Service (DBaaS), Storage as a Service (STaaS), Network as a Service (NaaS), and Security as a Service (SECaaS). By understanding the unique features and capabilities of each model, businesses can make informed decisions about leveraging the cloud to drive innovation, agility, and growth.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- IaaS represents the foundational layer of cloud computing, providing virtualized computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking infrastructure over the internet.
- With IaaS, organizations can dynamically scale their IT infrastructure based on demand, without the need for physical hardware investments.
- Key players in the IaaS space include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offering a wide range of services for building and managing scalable infrastructure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- PaaS abstracts away the complexity of infrastructure management, offering a complete platform and environment for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications.
- By providing tools and frameworks for application development, testing, and deployment, PaaS accelerates the software development lifecycle and enables faster time-to-market.
- Leading PaaS providers like Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Service offer a range of services tailored to developers’ needs, from database management to application scaling.
Software as a Service (SaaS):
- SaaS delivers fully functional software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, and upgrade software locally.
- With SaaS, organizations can access a wide range of applications, from productivity tools to enterprise software, without upfront investments in software licenses and infrastructure.
- Prominent SaaS providers such as Salesforce, Google Workspace, and Microsoft Office 365 offer a diverse portfolio of cloud-based applications to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS):
- DaaS provides virtual desktop environments accessible remotely over the internet, offering users a consistent desktop experience across devices.
- By centralizing desktop management and delivery, DaaS enables organizations to streamline IT operations, improve security, and support remote work initiatives.
- Leading DaaS providers like VMware Horizon Cloud, Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops, and Amazon WorkSpaces offer scalable solutions for desktop virtualization.
Function as a Service (FaaS):
- FaaS, also known as serverless computing, allows developers to deploy individual functions or code snippets as event-driven applications.
- By abstracting away infrastructure management and scaling, FaaS enables developers to focus on writing code and building applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
- Major FaaS providers such as AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Azure Functions offer a serverless computing platform for building and deploying applications at scale.
Backend as a Service (BaaS):
- BaaS offers backend services for mobile and web applications, including user authentication, database management, and push notifications.
- By leveraging pre-built backend infrastructure, BaaS accelerates app development, reduces time to market, and lowers development costs.
- Leading BaaS providers like Firebase, AWS Amplify, and Kinvey offer a range of services to support developers in building feature-rich and scalable applications.
Database as a Service (DBaaS):
- DBaaS provides managed database services over the cloud, handling database deployment, management, and scaling.
- By offloading database administration tasks to the cloud provider, organizations can focus on leveraging data to drive business insights and innovation.
- Key players in the DBaaS market, such as Amazon RDS, Azure SQL Database, and Google Cloud SQL, offer a variety of database engines and deployment options to meet diverse workload requirements.
Storage as a Service (STaaS):
- STaaS delivers cloud-based storage resources and services, allowing organizations to store and retrieve data over the internet.
- With STaaS, organizations can scale storage capacity on demand, optimize data storage costs, and ensure data availability and durability.
- Major STaaS providers like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Microsoft Azure Blob Storage offer a range of storage classes and features to meet the needs of diverse workloads and use cases.
Network as a Service (NaaS):
- NaaS offers networking infrastructure and services over the cloud, enabling organizations to provision, manage, and optimize network resources remotely.
- By abstracting away the complexities of network management, NaaS simplifies network operations, improves agility, and enhances security.
- Leading NaaS providers like AWS Direct Connect, Azure Virtual Network, and Google Cloud Interconnect offer a range of networking services, including virtual private networks (VPNs), bandwidth management, and network security.
Security as a Service (SECaaS):
- SECaaS provides security services over the cloud, including threat detection, encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and security monitoring.
- By leveraging cloud-based security solutions, organizations can enhance their security posture, detect and mitigate threats in real-time, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Major SECaaS providers such as Cisco Umbrella, Palo Alto Networks Prisma Cloud, and Microsoft Azure Security Center offer a comprehensive suite of security services to protect against evolving cyber threats.
In conclusion, cloud service models offer organizations the flexibility, scalability, and agility to innovate and transform their businesses. Whether it’s building scalable infrastructure, developing and deploying applications, or securing critical assets, the cloud provides a diverse set of services to meet the evolving needs of modern enterprises. By understanding the unique features and capabilities of each cloud service model, organizations can harness the power of the cloud to drive digital transformation and achieve their business objectives in a rapidly changing landscape.