Exploring the Cutting-Edge: Latest Technologies in the IT Industry
In the ever-evolving landscape of the information technology (IT) industry, it is important for businesses and professionals alike to stay abreast of the latest technological advancements. From artificial intelligence to quantum computing, a host of innovations are reshaping the way we work, interact, and solve complex problems. Let’s look at the ten most prominent technologies driving the IT industry forward.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI & ML)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have moved beyond mere buzzwords to become essential components of contemporary computing. AI algorithms enable machines to simulate human intelligence, while ML algorithms enable systems to learn from data and improve over time. Applications of AI and ML abound, from virtual assistants and chatbots to personalized recommendations and predictive analytics. As these technologies continue to mature, we can expect even more sophisticated applications in areas such as healthcare, finance, cybersecurity, and beyond.
2. Edge Computing
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has created a need for a shift toward edge computing, which enables data processing closer to the source. By reducing latency and bandwidth usage, edge computing facilitates real-time decision making and enhances the performance of IoT applications. Edge computing architecture distributes computing resources across a network of edge nodes, optimizing efficiency and scalability. Industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare will greatly benefit from the agility and responsiveness provided by edge computing solutions.
3. 5G Technology
The rollout of fifth generation (5G) cellular networks has ushered in a new era of connectivity featuring unprecedented speeds, low latency, and massive bandwidth. 5G technology enables faster data transfer rates, making it ideal for applications that require high throughput, such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgery. Beyond consumer applications, 5G networks are set to revolutionize industries ranging from telecommunications and entertainment to logistics and smart cities. The transformative potential of 5G is driving investment in infrastructure and driving innovation across sectors.
4. Blockchain
Originally conceived as the underlying technology behind Bitcoin, blockchain has emerged as a disruptive force with far-reaching implications beyond cryptocurrencies. Fundamentally, blockchain acts as a decentralized ledger that records transactions securely and transparently. This technology provides immutable data storage, verifiable trust, and tamper-proof transactions, making it suitable for applications such as supply chain management, digital identity verification, and smart contracts. As organizations recognize the benefits of blockchain in increasing transparency, efficiency, and security, its adoption is increasing across industries around the world.
5. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift in computational power, taking advantage of the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations at speeds faster than classical computers. Quantum bits or qubits, the fundamental units of quantum information, can exist in multiple states simultaneously, enabling parallel processing and exponential scaling. While practical quantum computers are still in the experimental stage, they promise to solve complex problems in cryptography, materials science, optimization and drug discovery that are beyond the reach of classical computers. As research advances and technological hurdles are overcome, quantum computing is set to revolutionize many fields.
6. Cybersecurity Innovations
In an era of growing cyber threats, cybersecurity remains a top priority for organizations seeking to protect their digital assets and sensitive information. Innovative cybersecurity solutions leverage artificial intelligence, machine learning, and behavioral analytics to detect and mitigate threats in real-time. Zero-trust security models, which assume that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, can be trusted by default, are gaining popularity as a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Additionally, decentralized identity solutions based on blockchain technology provide enhanced privacy and security by giving individuals control over their digital identity. As cyber threats constantly evolve, so too must the security measures taken to thwart them.
7. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic process automation (RPA) involves the use of software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive tasks and business processes. RPA technology mimics human interaction with digital systems, enabling organizations to streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve productivity. By automating mundane and rules-based tasks, RPA frees up human resources to focus on more creative and value-added activities. Industries ranging from finance and healthcare to manufacturing and customer service are leveraging RPA to achieve operational efficiencies and cost savings. As RPA platforms evolve to incorporate artificial intelligence and cognitive capabilities, the scope of automation is poised to expand further.
8. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies are blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds, creating immersive experiences that transcend traditional boundaries. AR overlays digital content on the real world, enhancing perception and interaction, while VR immerses users completely in a virtual environment. From gaming and entertainment to education and training, AR and VR applications span a wide variety of industries. In health care, surgeons use AR to visualize a patient’s anatomy during procedures, while architects use VR to explore virtual building designs. As AR and VR hardware becomes more accessible and software development tools evolve, the potential for transformative experiences continues to grow.
9. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem consists of interconnected devices equipped with sensors, actuators, and communication capabilities, enabling them to collect and exchange data. Applications of IoT include smart homes, wearable devices, industrial automation, and the development of smart cities. By using IoT data, organizations can optimize processes, improve decision making, and enhance customer experiences. However, the proliferation of IoT devices also presents challenges related to data privacy, security, and interoperability. As IoT technologies mature and standards evolve, addressing these challenges will be critical to unlocking the full potential of the IoT revolution.
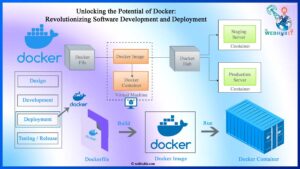
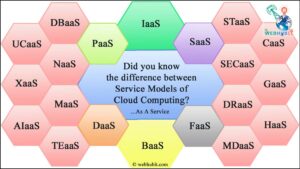
10. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing remains a cornerstone of digital transformation, providing scalable and on-demand access to computing resources over the Internet. Cloud services include infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS), providing organizations with flexibility, agility, and cost efficiency. Serverless computing, a cloud computing model in which cloud providers dynamically manage the allocation of machine resources, is gaining popularity due to its scalability and cost-effectiveness. Multi-cloud strategies, which involve distributing workloads among multiple cloud providers, provide redundancy, flexibility, and vendor diversity. Containerization technologies like Kubernetes enable organizations to seamlessly deploy and manage applications in cloud environments. As cloud computing continues to grow, it continues to be a catalyst for innovation and digital disruption across industries.
In conclusion, the latest technologies are bringing unprecedented levels of innovation, disruption and change to the IT industry. From artificial intelligence and edge computing to quantum computing and blockchain, these technologies have the potential to reshape the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. As organizations adopt these technologies and harness their capabilities, they will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.